Last summer, I posted a substack on the newly approved RSV vaccines for adults ages 60 years and older – RSVPreF3 (Arexvy, GSK) and RSVpreF (Abrysvo, Pfizer).If you missed it, you can find it here. This Eye on the Evidence will look at and UPDATE the new RSV vaccines that will target newborns, toddlers, and pregnant women.
This is an additional update. There is a BIG PUSH for RSV shots for all ages this fall. Learn why you should say no!
PLEASE FEEL FREE TO PRINT THIS FOR YOUR FRIENDS AND FAMILY!
===========================================
QUICK LINKS:
Follow: Twitter | Instagram | Telegram | Truth Social | Podcast Membership|
Broadcasts: Rumble| HappyHour |This Wk wDrT | Brighteon | Bitchute | Tues Coffee
Learn about ECP: Health Center Cleveland, OH | Health Center Ventura, CA
Websites: DrTenpenny.com |Tenpenny Apparel| Tenpenny Supplements
============================================
What is RSV?
Respiratory syncytial (sin-SISH-uhl) virus, or RSV, is a common respiratory virus that usually causes mild, cold-like symptoms. According to the CDC, RSV is the most common cause of bronchiolitis (inflammation of the small airways in the lung) and pneumonia (infection of the lungs) in children less than 1 year of age in the United States. In fact, RSV is SO common that almost all children will have had an RSV infection – and acquired natural immunity - by the time they are 2 years old.
In May 2022, two new adult RSV vaccines were released for use in adults over 60 years of age. GSK released Arexvy and three weeks later, the FDA approved Pfizer’s RSV vaccine for adults. Abrysvo. (where do they come up with these confusing names?)
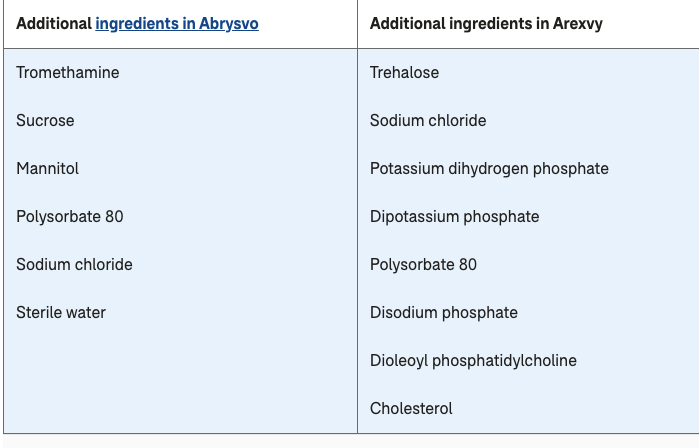
Arexvy contains preF proteins but is not considered to be a bivalent vaccine. It contains preF proteins from two RSV subtypes RSV A and RSV B, but not the viral sequence. Abrysvo is a bivalent vaccine. It is also approved for use in pregnant women to protect newborns after birth.
Another difference between the RSV vaccines is that Arexvy contains the adjuvant, polysorbate 80 to which upwards of Abrysvo does not. Adjuvants are substances that are sometimes added to vaccines to help them work better by increasing the body’s inflammatory response.
Abrysvo and Arexvy haven’t been directly compared to each other, so it is not known if one vaccine works better than the other. Combined, they were tested on about 30,000 people - and now they are leased to the world for real-life clinical trial. Sound familiar?
UPDATE ON RSV VACCINATION IN ADULTS
Myocarditis is defined as the inflammation of cardiac muscle causing myocellular damage leading to cardiac dysfunction and possibly heart failure. Viral infections are considered to be the most common etiology of myocarditis. Although your doctor may try to convince you otherwise, RSV-associated myocarditis is a rare cause of viral myocarditis in the adult population.
This is only the first season of RSV vaccine availability for adults, but the uptake has been quite low, at barely 20% nationwide, even in those 80 years of age and older.
SOURCE: CDC WEBSITE
Pregnant Women
Sandwiched in between those two RSV vaccine approvals for adults, an FDA panel voted on May 18, 2023, to approve the RSV vaccine for pregnant women; the idea is to inject pregnant women so that infants aged up to 6 months will be protected.
According to an article in The Lancet Microbe (here’s the full study published April, 2023 in The New England Journal of Medicine):
The maternal RSV vaccine was assessed in an international, phase 3, randomized trial of women at 24 to 36 weeks gestation. The vaccine was given to 3,682 participants, while 3,676 received a placebo. In the study, medically attended RSV occurred within 90 days of birth in 24 infants of women in the vaccine group and in 56 infants of women in the placebo group (vaccine efficacy, 57.1%). These results did not meet the statistical success criterion.
Medically attended RSV-associated lower respiratory tract illness is defined as RSV-positive respiratory illness in which the patient needs to be seen in a physician's office, an emergency department, or a hospital.
The incidences of adverse events reported within 1 month after injection or within 1 month after birth were similar in the vaccine group (13.8% of women and 37.1% of infants) and the placebo group (13.1% and 34.5%, respectively).
These stats make me wonder what was actually in the ‘placebo.’ Not surprisingly, the placebo’s identity is not found anywhere, not even at ClinicalTrials.gov, where the study design was outlined. After much digging, I found that the PLACEBO contained aluminum hydroxide. At the same time, FDA advisers expressed frustration that Pfizer’s final phase 3 trial wasn’t large enough to know whether the increased rate of preterm labor in the vaccinated group compared with the placebo group—5.7% versus 4.7%—was statistically significant. (What??!! Could handwashing and vitamin C do as well or better?)
In May 2023, the FDA approved RSVpreF under the name ABRYSVO for the prevention of RSV in individuals 60 years of age or older, another Pfizer vaccine with little research to back it up long-term. The FDA does what its Boss (big pharma) tells it to do. After all, the FDA needs to keep its paycheck, too.
FDA’s budget from FY 1992 through FY 2020 and the relative portion of the budget that is made up of user fees versus budget authority. We see that the FDA’s budget has risen over time, with the greatest increases due to user fees rather than increases in budget authority [from Congress]. Specifically, FDA’s budget has grown from just under $1 billion in FY 1992, when it was entirely budget authority, to almost $6 billion in FY 2020, approximately $3 billion of which was for user fees.
UPDATE ON RSV VACCINE FOR PREGNANT WOMEN
The CDC has created a monitoring page called, ‘The Weekly RSV Vaccination Dashboard.’ It is designed to track weekly RSV vaccination data obtained from a variety of data sources, including surveys, healthcare claims, electronic medical records, and the Immunization Information System’s (IIS) data.
The IIS datasets are population-based, computerized databases that record all vaccine doses administered by participating providers to persons residing within a given geopolitical area. All 50 states and all US-protected states, such as Puerto Rico, Guam, and American Samoa, are part of the IIS tracking system. A physician can access the IIS database to determine what vaccines have been given, and what vaccines are needed.
At the population level, the IIS provides aggregate data on vaccinations for use in surveillance. It allows public health officials to identify “susceptible persons” – remember that means UNVACCINATED - with the goals of improving vaccination rates and reducing vaccine-preventable disease.
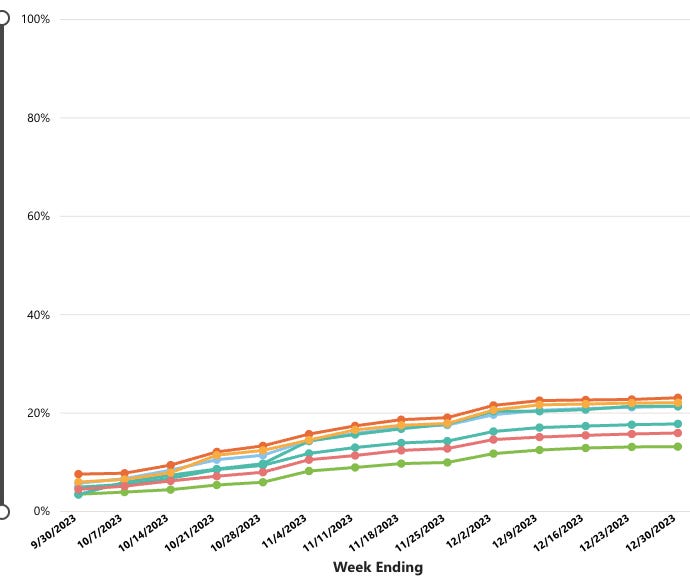
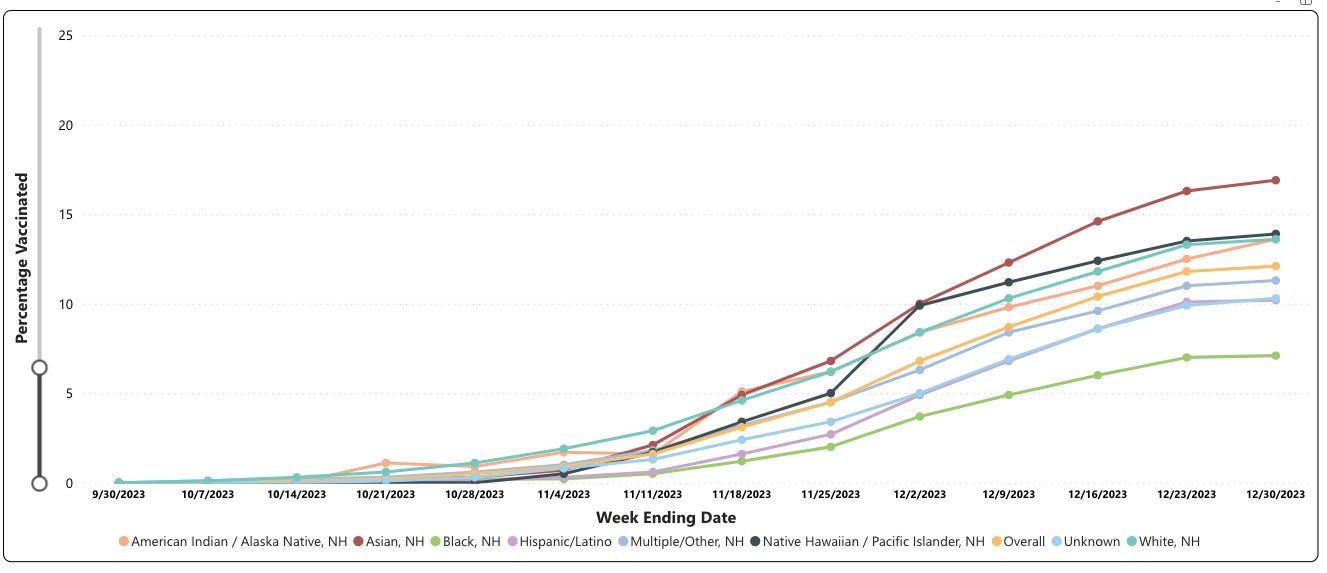
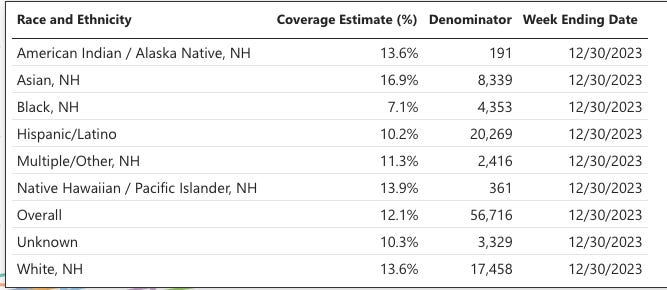
As of December 30, 2023, among persons who were pregnant and ≥32 weeks gestation as of September 22, 2023, coverage with the RSV vaccine was only 12.1%.
Vaccination coverage was highest among non-Hispanic Asian (16.9%) pregnant persons and lowest among non-Hispanic Black (7.1%) pregnant persons. I would say the uptake of their new “billion-dollar” vaccine has been a dud in this population. Thank goodness!
Source: CDC website - RSV
Source: CDC website - RSV
Another Shot for Newborns
Previous efforts to develop an RSV vaccine for children were unsuccessful. In fact, the first RSV vaccine, developed in the 1960s, actually caused a severe reaction in the lungs when children were exposed to RSV in circulation, leading to two infant deaths. Alternative RSV vaccine development was hindered by this result for decades, a process that was most likely akin to ADE = antibody dependent enhancement.
But AstraZeneca found a way to bypass the usual slow-go vaccine approval process – and even got the product fast tracked to release - by instead developing a monoclonal antibody against RSV.
The use of monoclonal antibodies to address RSV isn’t new. In fact, Synagis (palivizumab) is a monoclonal antibody that has been used for more than 20 years. The downside of Synagis is that it must be administered as five separate doses (one dose per month for 5 months), and it is very expensive: one dose is around $1,900USD. Therefore, it is only used in high-risk preterm infants. Beyfortus, the new RSV monoclonal, is recommended as a single injection and is anticipated to cost $600 in the US and $300 in Europe.
AstraZeneca and Sanofi, of course, are pushing for Beyfotus to be used in all children not just those at high or higher risk, which could be up to 3.5 million infants per year. This would generate potential revenue of over $1.1 billion.
According to the product monograph, Beyfortus (nirsevimab), which was FDA- approved July 17, 2023, is indicated for neonates and infants up to 24 months of age. It is also indicated for children with congenital heart disease, cystic fibrosis, Down syndrome, and other types of immunocompromising diseases.
What is interesting about this injectable product is that children who are most at risk for serious RSV illness - premies (born before 37 weeks) and ultra-premies (born before 28 weeks) gestation – are not currently included in the recommendations for this shot.
This is from the Product Monograph
The safety and efficacy of BEYFORTUS in children older than 24 months of age have not been established.
The safety and efficacy of BEYFORTUS in infants with body weight below 1.6 kg have not been established.
Dosing in infants with a body weight from 1.0 kg to <1.6 kg is based on extrapolation.
The efficacy of BEYFORTUS in infants who remain vulnerable to severe RSV disease during their first or second RSV season has not been directly established and is based on extrapolation of exposure only.
There is limited information available in extremely preterm infants (Gestational Age <29 weeks [ultra-premies]), and no clinical data are available in infants with a postmenstrual age (gestational age at birth plus chronological age) of 32 weeks.
Limited data are available in infants with Down syndrome (n=13), cystic fibrosis (n=5), congenital airway anomalies (n=9), and neuromuscular disease (n=0; not evaluated in clinical trials).
Well, isn’t that interesting...? NO data. FEW studies. FEW participants. But in the introduction of the monograph, the monoclonal antibody for RSV is recommended for these groups anyway.
Hmm.
AND it is recommended that this shot be given at birth if the baby is born during ‘RSV season,’ which typically starts during the fall and peaks in the winter. This is recommended even though Beyfortus treatment had no effect on hospitalization rates, which is the primary reason to give the injection.
In two of the preliminary studies, infants given Beyfortus had a huge uptick in RSV neutralizing antibody levels. Approximately 5 months after the shots, infants were found to have antibody levels more than 50 times higher than baseline levels and after the first year (360 days), the levels remained approximately 7 times higher than baseline. Investigators concluded (pg 12) that the Beyfortus provides antibody protection for at least 5 months.
UPDATE ON RSV SHOTS FOR INFANTS = Beyfortus (nirsevimab)
Convincing pregnant women or those women trying to get pregnant to give their newborns ANOTHER injection has not been particularly successful. As of the end of November 2023, when 336 pregnant women were asked about this injection, this was the result:
Only about 31% said they would definitely give their newborn this jab. Granted, the sample size was quite small, but this was not an overwhelming response to the new injection. Yeah!!
Is preventing RSV a good thing?
eBook: The Importance of Fever
Given the fact that most children have had and have recovered from an RSV infection by the time they are 2 years of age, how does preventing this infection bode for their long-term immunity as they get older? Will these extraordinarily high and sustained levels of antibody lead to autoimmune disease through molecular mimicry?
When monoclonal antibodies were first developed against the SARS-CoV2 spike protein, the antibody cross-reacted with 28 out of 55 tissue antigens. The tissue groups that included gut and barrier proteins, gastrointestinal system cells, thyroid, nervous system, heart, joint, skin, muscle, mitochondria and liver tissues, and antigens used for the screening of autoimmune diseases.
The human monoclonal antibodies used in the study were almost identical with antibodies found in persons recovered from illness. Thus, the results established the potential risk for autoimmunity and multisystem disorders that came from cross-reactivity between human tissues and the monoclonal antibody.
Since this product was fast-tracked into production, there are no long term studies. We are unleashing all these products on newborns, pregnant women, and the elderly with no long-term studies. Does this sound familiar?
Common Sense Options and Solutions
Will we fall for more ‘vaccination nation’ tactics or do simple, common-sense things instead:
Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your upper shirt sleeve when coughing or sneezing.
Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. If soap and water are not available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
Clean touched surfaces, such as doorknobs, keyboards, and mobile devices frequently.
Avoid close contact, such as kissing, shaking hands, and sharing cups and eating utensils with others if you are ill. And stay home! Kinda silly to have to remind people of this, but it is important.
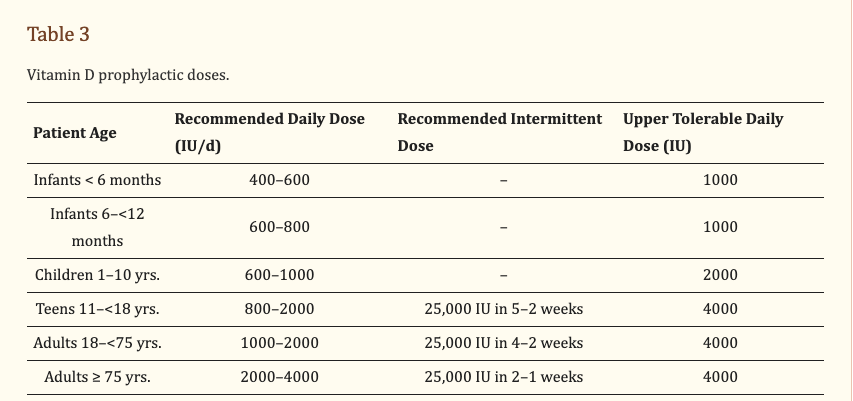
Vitamin D drops for the kiddos will keep them healthy all winter long. The advantage of drops is they are easy to administer and can adjust the number of drops based on age and weight.
Table from this (good) article:
Take your supplements regularly: OptiMune, one of our best sellers, has everything you need in just two convenient capsules: Vitamin D, Vitamin C, zinc, quercetin and NAC. Or for kids, you can get the chewable version.
As an adult, keep Vitamin D 50,000 IU and Opti-Early Vira Relief in your cupboard to stop any viral infection in its track when symptoms start.
Don’t fall for this fear-based push for yet another barely-studied set of vaccines for an infection that is another version of the common cold.















My friend, who is 70, got the RSV vaccine, got RSV and got very sick . Next, he developed a heart problem. Next, he got a huge cancerous growth on his neck. Vaccines are evil and intended to harm, kill, or create life-long patients.
People need to question WHY is this vaccine needed if not properly tested with long-term trial data. Stop believing in the fear-porn and stop taking vaccinations for every disease they shove our way. Let your immune system handle it.